Parts Parts And Functions Of A Microscope
The microscope in Figure 1 is illuminated through the oil lamp and water-filled spherical reservoir (also illustrated in Figure 1). Light from the lamp is diffused when it passes through the reservoir and is then focused onto the specimen with a lens attached to the reservoir. This early microscope suffered from chromatic (and spherical.
The Wonders Of Microscopes What You Need To Know Creyentes Diverses News
Microscope - Types, Diagrams and Functions By Editorial Board October 13, 2022 Microscope - Let's split the name into two parts to understand what it actually means. " Micro " means very small (typically not visible to the naked eye) and " scope " means to assess or investigate carefully.

301 Moved Permanently
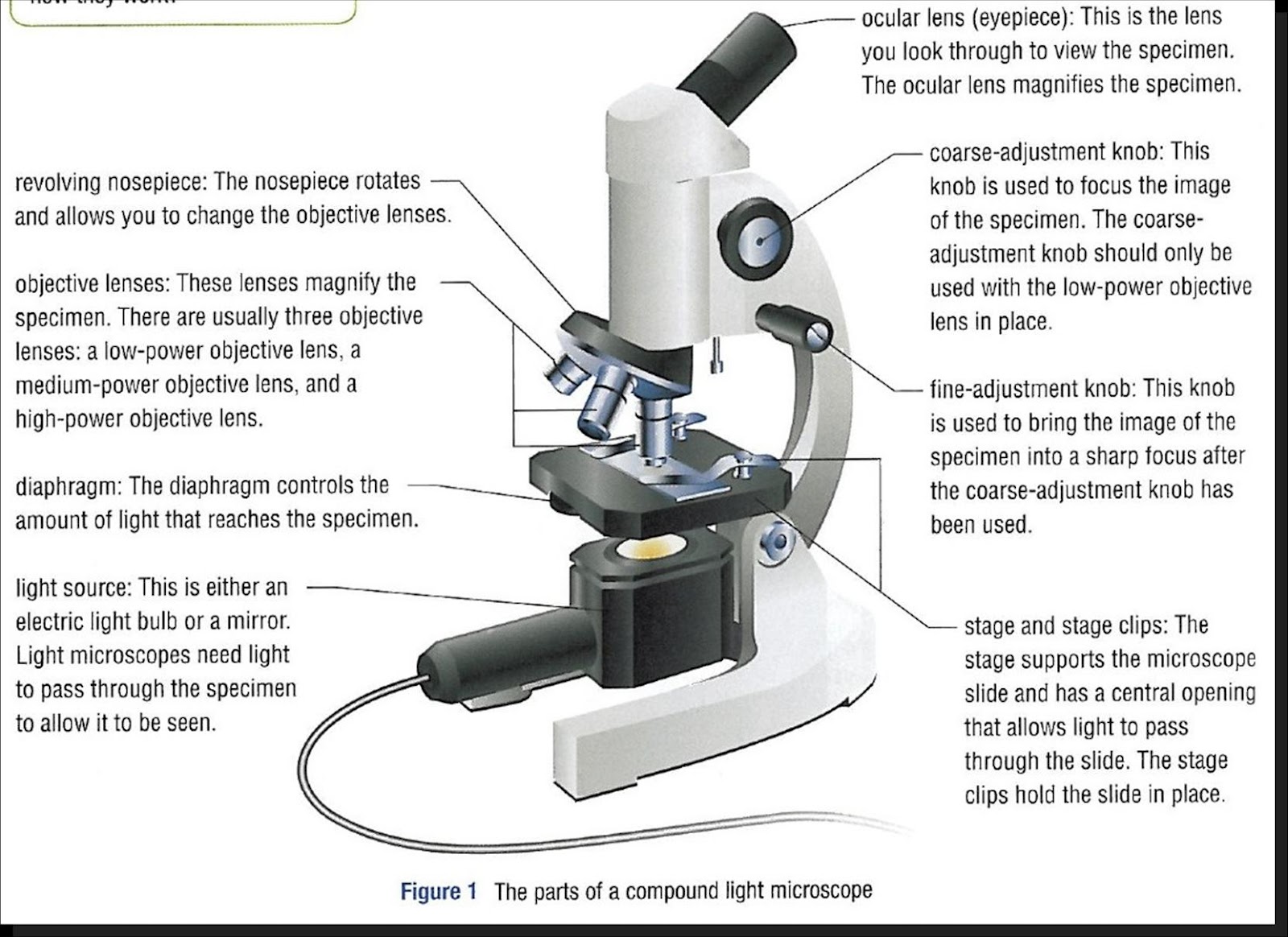
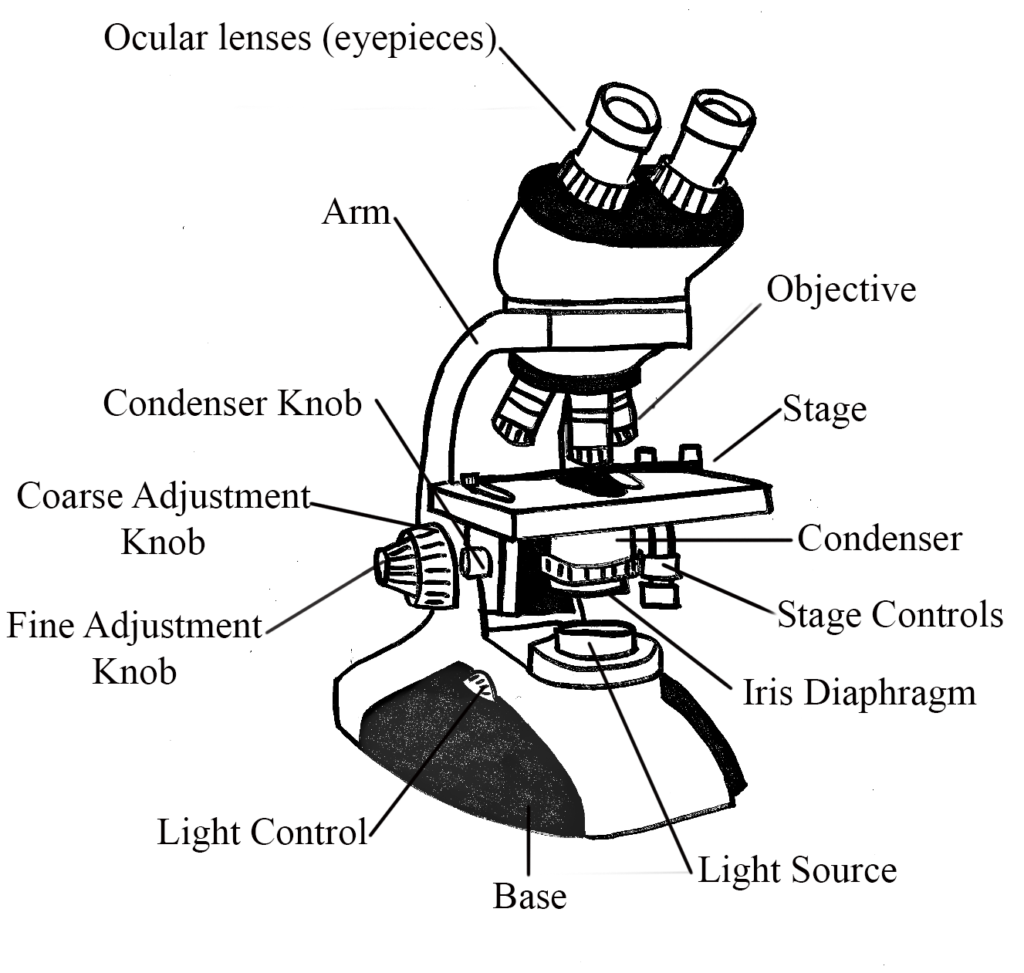
Iris diaphragm: Adjusts the amount of light that reaches the specimen. Condenser: Gathers and focuses light from the illuminator onto the specimen being viewed. Base: The base supports the microscope and it's where illuminator is located. How Does a Compound Microscope Work?
How to Use a Microscope
Simple Microscope Diagram (Parts) with Labels Frequently Asked Questions Definition and Working principle Simple microscope is a magnification apparatus that uses a combination of double convex lens to form an enlarged, erect image of a specimen.
Microscopes General Microbiology
The optical microscope often referred to as the light microscope, is a type of microscope that uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images of small subjects. There are two basic types of optical microscopes: Simple microscopes. Compound microscopes. The term "compound" in compound microscopes refers to the microscope having.

The Parts of a Compound Microscope and How To Handle Them Correctly
The web page titled "Parts of a Microscope with Labeled Diagram and Functions" has the following key takeaways: 🔍 The microscope is an essential tool for scientists, researchers, and medical professionals. 🧬 The main function of a microscope is to provide a magnified view of small objects or organisms, such as bacteria, cells, or tissues.

Clipart microscope parts labeled WikiClipArt
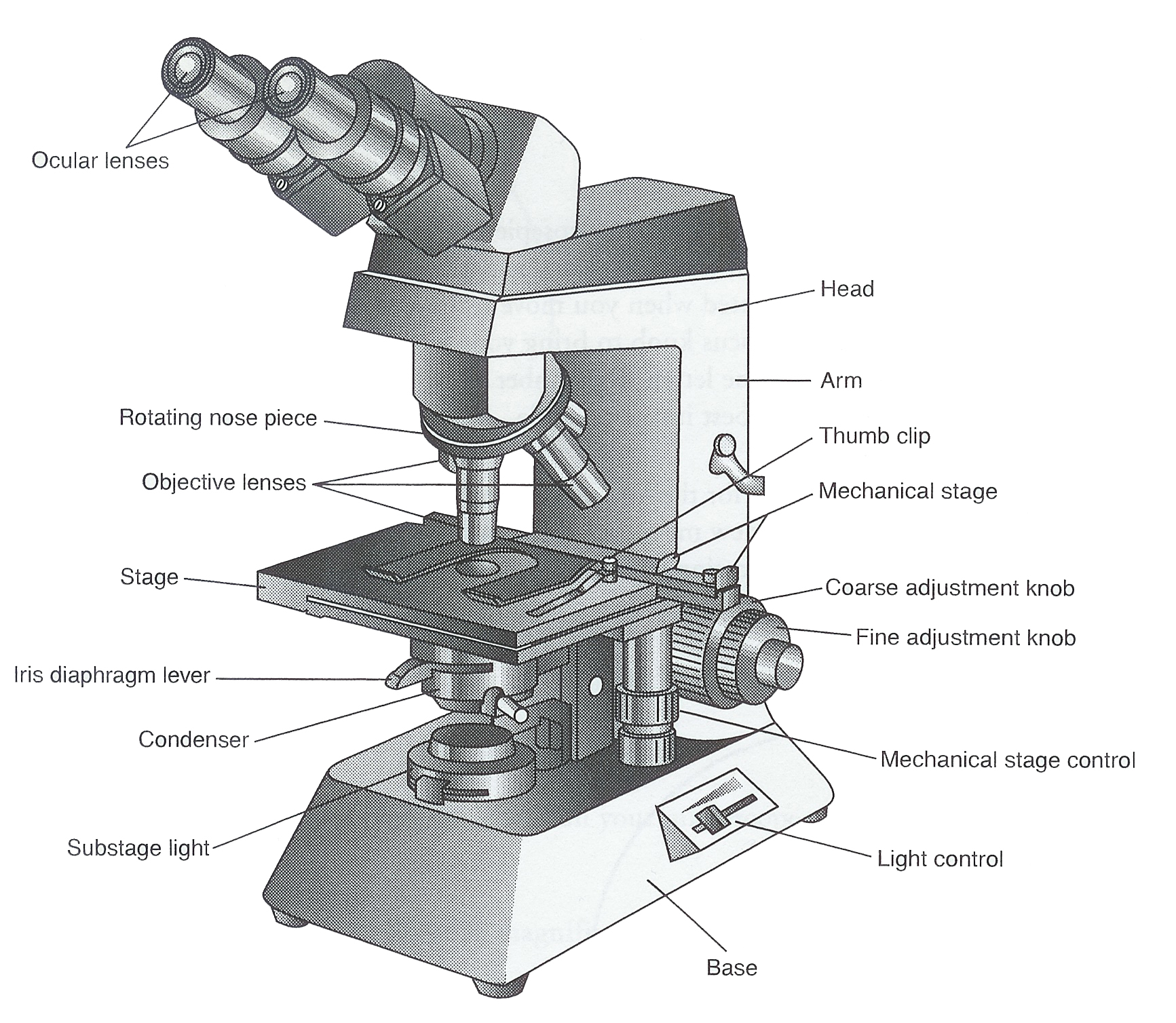
There are three major structural parts of a compound microscope. The head includes the upper part of the microscope, which houses the most critical optical components, and the eyepiece tube of the microscope. The base acts as the foundation of microscopes and houses the illuminator. The arm connects between the base and the head parts.

Parts of a microscope with functions and labeled diagram
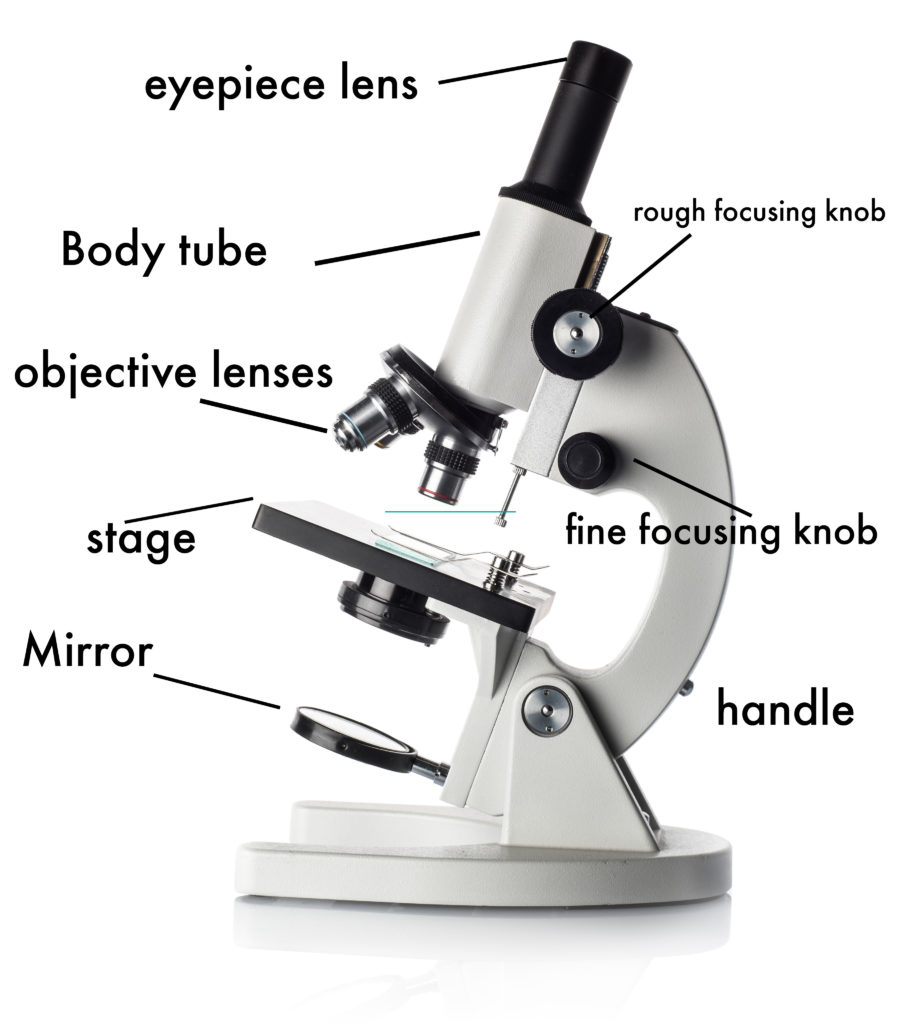
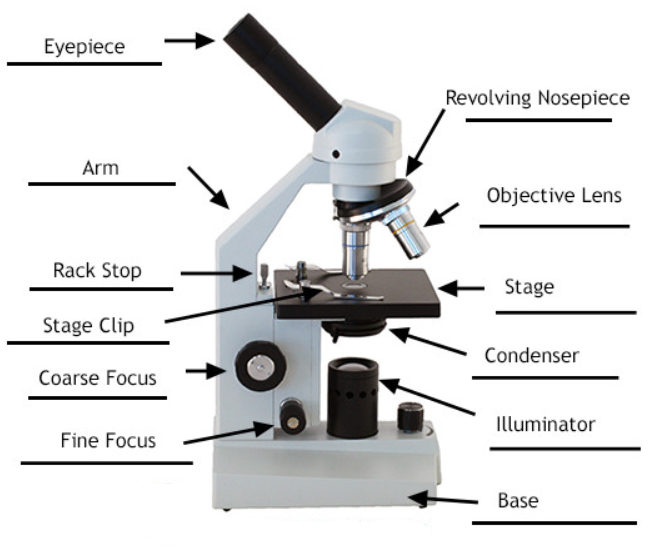
1. Eyepiece or Ocular Lens Eyepiece lens magnifies the image of the specimen. This part is also known as ocular. Most school microscopes have an eyepiece with 10X magnification. 2. Eyepiece Tube or Body Tube The tube hold the eyepiece. 3. Nosepiece Nosepiece holds the objective lenses and is sometimes called a revolving turret.
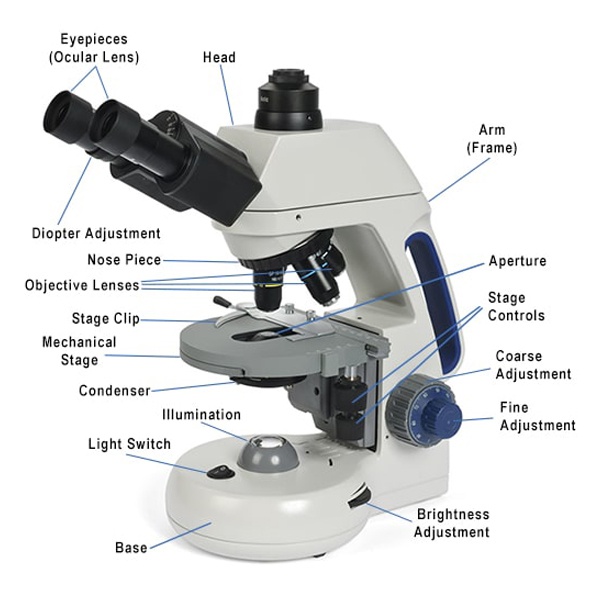
How to Use a Microscope (Properly) Step by Step New York Microscope
Explore the different parts of a microscope using a diagram, including the microscope lens, eyepiece, and stage. Updated: 10/13/2022 Create an account
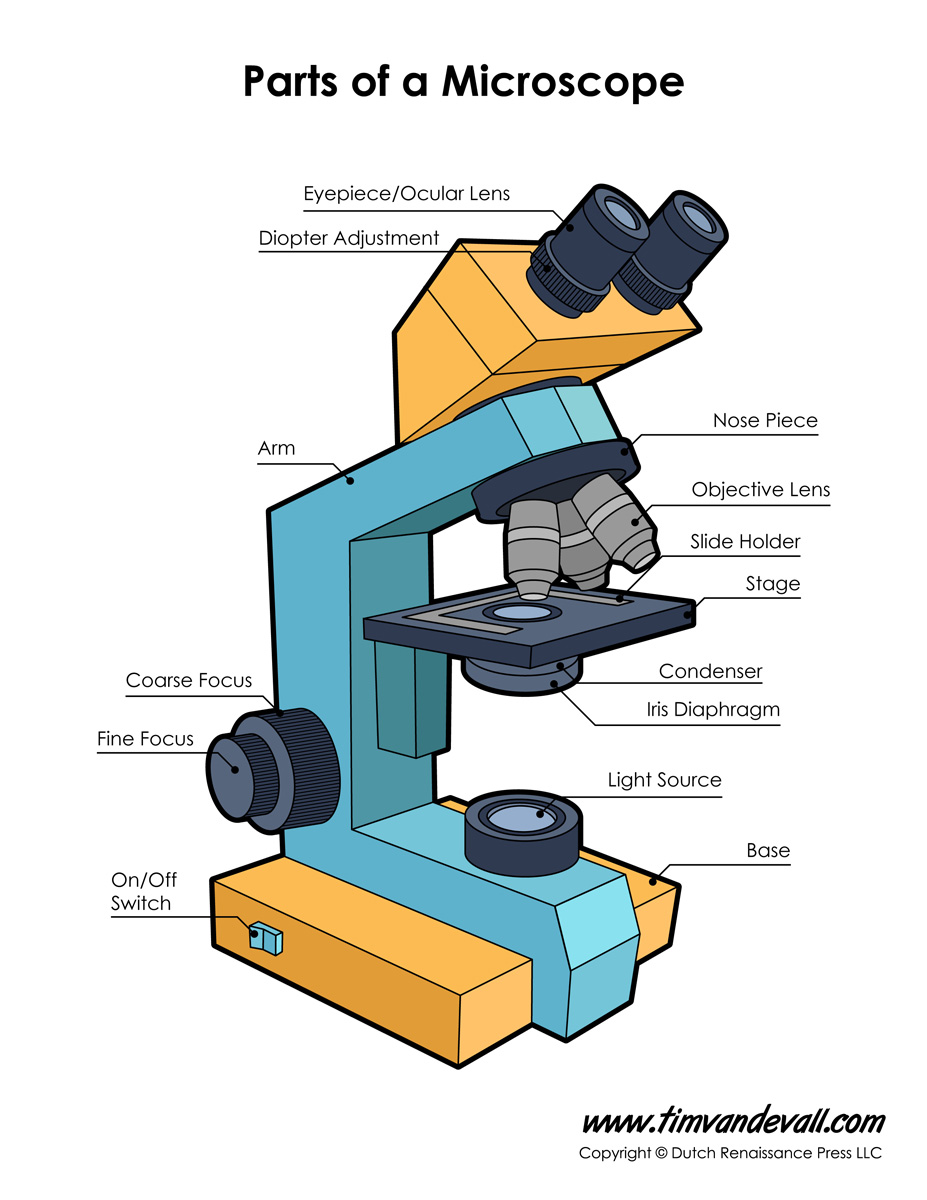
Monday September 25 Parts of a Compound Light Microscope
A labeled diagram of microscope parts furnishes comprehensive information regarding their composition and spatial arrangement within the microscope, enabling researchers to comprehend their function effectively. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricate parts of the microscope, exploring their functions in detail.
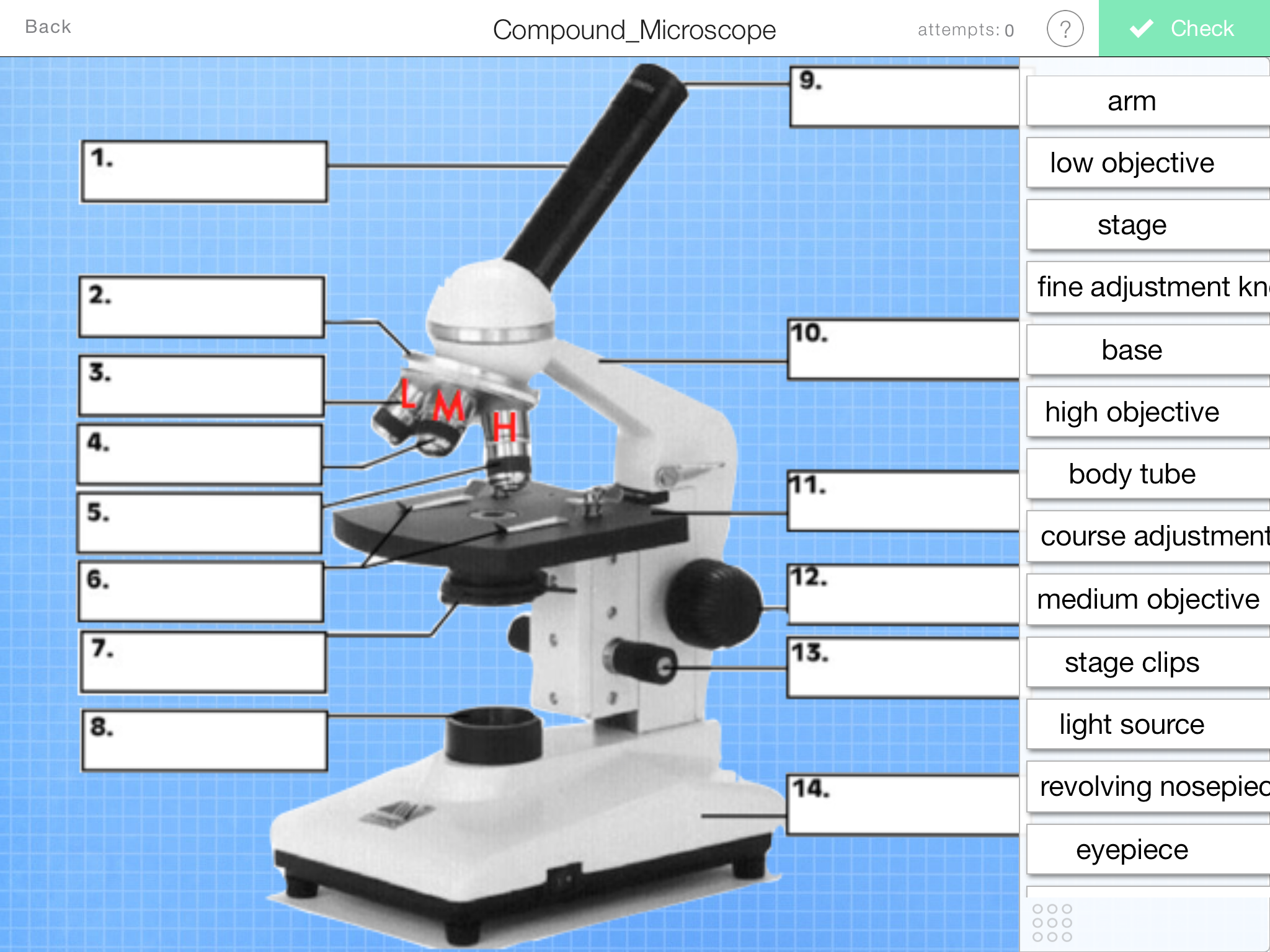
Parts of a Compound Microscope — Learning in Hand with Tony Vincent
Magnification is a measure of how much larger a microscope (or set of lenses within a microscope) causes an object to appear. For instance, the light microscopes typically used in high schools and colleges magnify up to about 400 times actual size. So, something that was 1 mm wide in real life would be 400 mm wide in the microscope image.
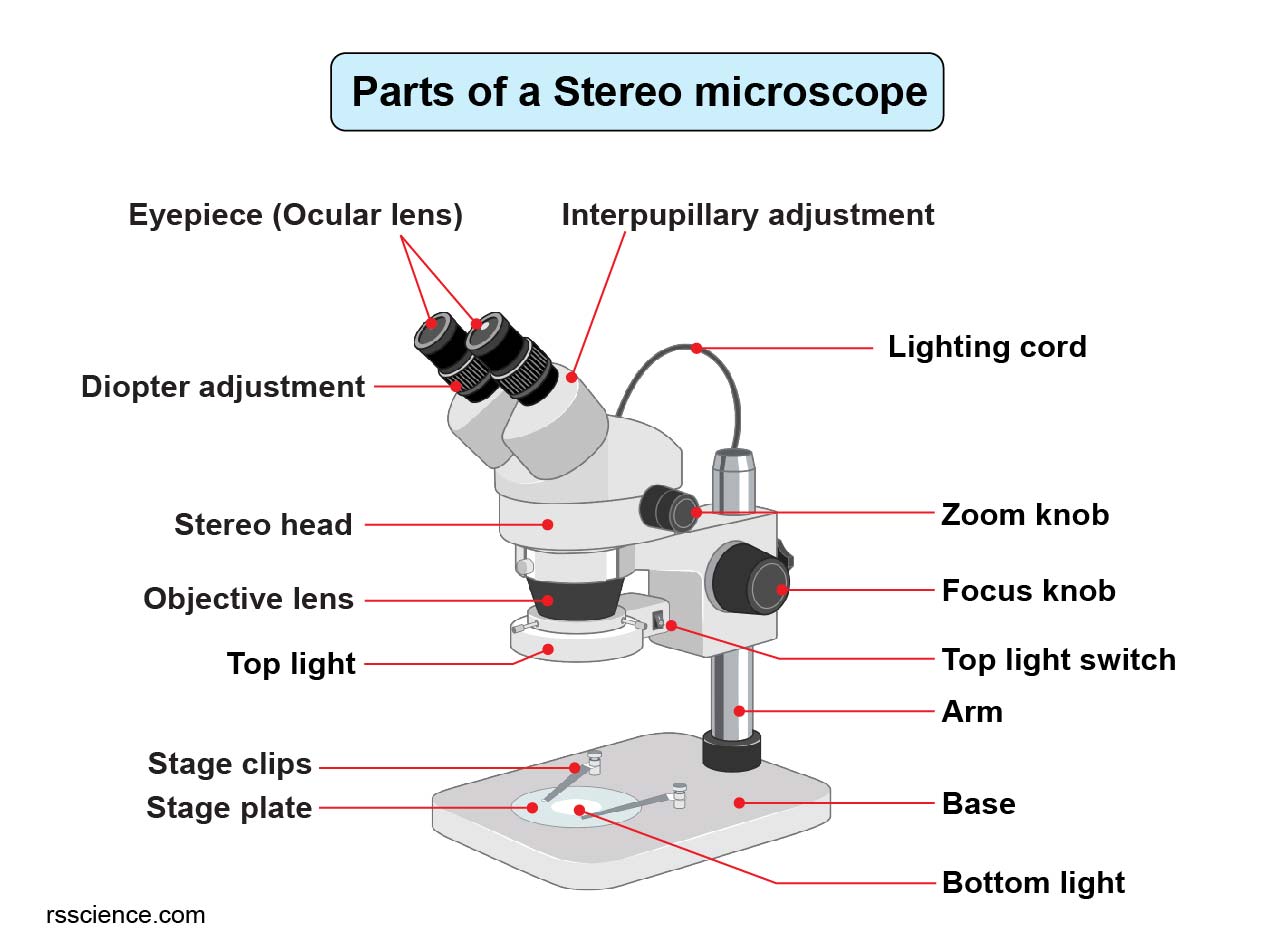
Parts of Stereo Microscope (Dissecting microscope) labeled diagram
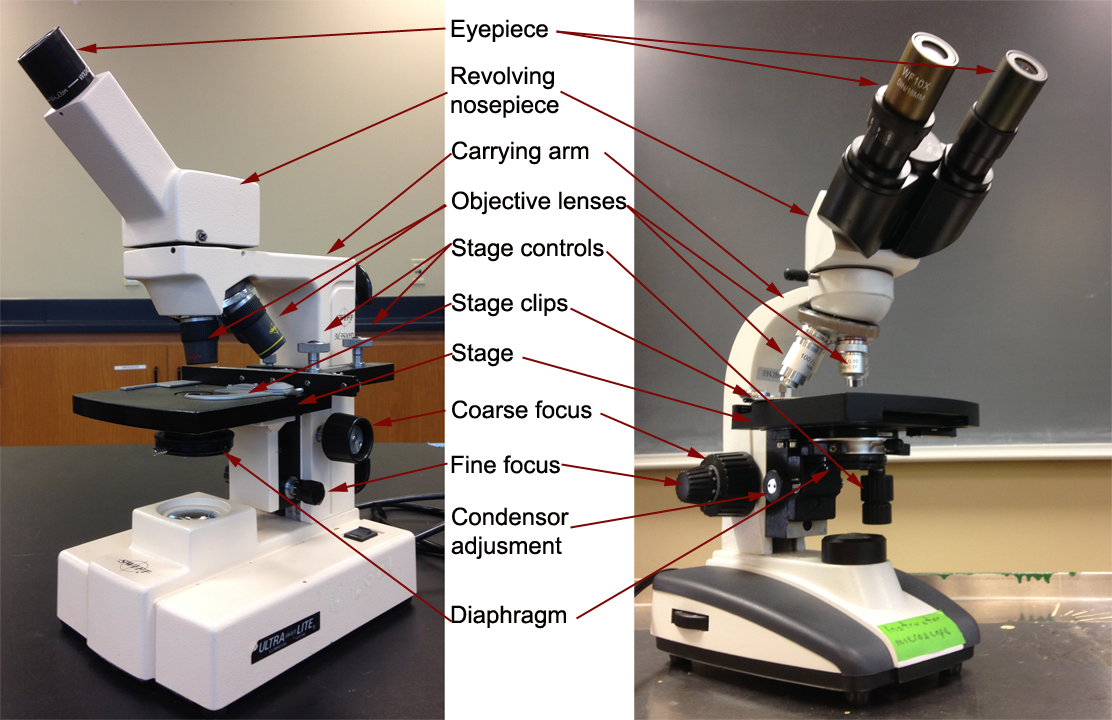
1. Eyepiece 2. Body tube/Head 3. Turret/Nose piece 4. Objective lenses 5. Knobs (fine and coarse) 6. Stage and stage clips 7. Aperture 9. Condenser 10. Condenser focus knob 11. Iris diaphragm 12. Diopter adjustment 13. Arm 14. Specimen/slide 15. Stage control/stage height adjustment 16. On and off switch 17. Base

Parts of a Microscope The Comprehensive Guide Microscope and
Parts of the Microscope (Labeled Diagrams) By Editorial Board December 14, 2022 The microscope is one of the must-have laboratory tools because of its ability to observe minute objects, usually living organisms that cannot be seen by the naked eyes. It is categorized into two: simple and compound microscopes.

Microscope diagram Tom Butler Technical Drawing and Illustration
Diaphragm (Iris) Condenser Aperture Stage Objective lens Body Tube Ocular Lens (eye-piece) Coarse and Fine Adjustment Knob Arm Base Microscope Worksheet The Light Microscope Light microscopes are used to examine cells at relatively low magnifications. Magnifications of about 2000X are the upper limit for light microscopes.
1.5 Microscopy Biology LibreTexts
Place the slide on the stage and secure it with the stage clip.; Use the coarse focus knob to move the stage as high as it can go. Use stage adjustment knobs to center the "e" so that the light from the light source can pass through it.; Looking through the ocular lenses, lower the stage with the coarse focus adjustment knob until the "e" comes into view.
Parts of a Compound Microscope Labeled (with diagrams) Medical
The hand magnifying glass can magnify about 3 to 20×. Single-lensed simple microscopes can magnify up to 300×—and are capable of revealing bacteria —while compound microscopes can magnify up to 2,000×. A simple microscope can resolve below 1 micrometre (μm; one millionth of a metre); a compound microscope can resolve down to about 0.2 μm.